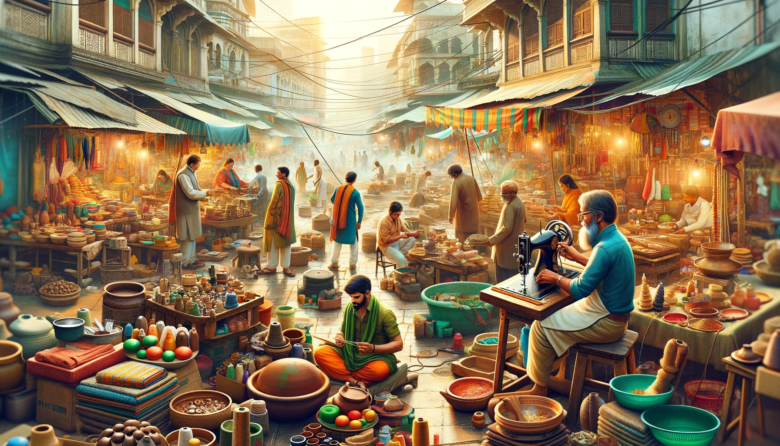
In the bustling streets and rural landscapes of India, an economic powerhouse thrives beyond the structured confines of formal employment. This is the realm of the informal sector, a crucial yet often overlooked component of the Indian economy. In this two-part series, we dive into the complexities of this sector, exploring its vastness, contributions, challenges, and the path forward.
The Essence of the Informal Sector
What is the Informal Sector?
The informal sector, often synonymous with the unorganized sector, comprises businesses and employment opportunities that are not regulated by the government. This includes a wide range of activities, from street vending to small-scale manufacturing, where workers do not have formal employment status.
Size and Scope
India’s informal sector is monumental, both in terms of its size and its contribution to the economy. It’s estimated that over 80% of India’s workforce is employed in the informal sector, supporting possibly 400 million livelihoods.
Demographics and Distribution
Workforce Composition
The informal sector in India is characterized by diverse demographics:
- A significant proportion of the workforce is young, with 61.72% aged between 18 and 40 years.
- Women play a pivotal role, constituting a substantial portion of the workforce, especially in sectors like domestic work and agriculture.
Geographical Spread
The informal economy spans urban and rural areas, with no region or sector exempt from its presence. From agriculture in rural India to urban street markets, the informal sector’s reach is extensive.
Economic Contributions and Challenges
GDP Contribution
Despite its unregulated nature, the informal sector is a significant contributor to India’s GDP, accounting for about half of the country’s economic output.
Employment Generator
It’s a primary source of livelihood for millions, especially in times of economic downturns or crises like the COVID-19 pandemic.
Challenges Faced
Workers in the informal sector often grapple with low income, lack of job security, and minimal access to social security benefits. The sector also faces challenges in embracing digitalization and accessing capital and credit.
Recent Developments
Social Security and Digital Adoption
Recent initiatives, like the introduction of a social security fund for informal workers, mark significant strides towards addressing the sector’s challenges. Moreover, the adoption of digital payment systems has shown promise in enhancing productivity and sales for informal businesses.
Conclusion
The informal sector in India, with its vast workforce and significant economic contribution, is an integral part of the nation’s economic fabric. However, the challenges it faces require concerted efforts from policymakers, entrepreneurs, and social organizations to ensure its sustainable development.
Author’s Note: This blog aims to shed light on the often underrepresented yet vital informal sector of the Indian economy. In our next part, we will delve deeper into government policies, the path to formalization, and the future prospects of this sector.
G. C., Ecosociosphere contributor.
References
- Business Upturn. “Empowering India’s informal workforce: Budget 2024 set to introduce social security fund.” (2024)
- Emerald Insight. “Informal sector in India and adoption of digital technologies.” (2024)
- ForumIAS. “India’s informal economy: Challenges and solutions – Explained, pointwise.” (2024)
- NextIAS. “Informal Sector – Current Affairs.” (2022)




Comments
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me.
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good. https://accounts.binance.com/zh-CN/register?ref=VDVEQ78S
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me?
Hello men
Good evening. A 14 great site 1 that I found on the Internet.
Check out this site. There’s a great article there. https://appsandapplications.com/storytelling-in-videogames/|
There is sure to be a lot of useful and interesting information for you here.
You’ll find everything you need and more. Feel free to follow the link below.