Have you ever wondered how your heart tirelessly keeps beating, day in and day out, ensuring that your body stays alive and well? The science behind how the heart functions is captivating and is essential for ensuring good cardiac health. Understanding how the heart works, from its rhythmic contractions to the way blood flows through your body, can give us valuable insights into how we can keep it healthy and avoid issues like heart disease. In this blog, we’ll dive into the science of how the heart functions, exploring its relationship with physics and what it means for cardiac health.
The Physics of Heart Function
At the core of heart function is a finely tuned system governed by the principles of physics. Let’s break it down into some essential concepts:
Pressure and Flow: The Mechanics of Blood Circulation
The heart is essentially a pump that circulates blood throughout the body. It uses pressure differences to move blood through the circulatory system, similar to how a water pump moves water through pipes. Blood moves from areas of high pressure (in the heart) to areas of low pressure (in the veins and arteries), creating a continuous flow. This pressure is generated by the heart’s contractions, specifically in the ventricles (the lower chambers of the heart). During systole, the phase when the heart contracts, pressure in the ventricles rises, forcing blood into the arteries. When it relaxes during diastole (the phase when the heart muscle relaxes), the pressure decreases, allowing blood to fill the heart again.
In healthy individuals, this balance between pressure and flow is efficient and smooth. However, if blood vessels become narrowed due to atherosclerosis (plaque build-up), the heart has to work harder to pump blood, leading to hypertension (high blood pressure).
Electrical Impulses: The Heart’s Pacemaker
The heart’s rhythm is controlled by a natural electrical system. At the centre of this system is the sinoatrial (SA) node, often referred to as the heart’s pacemaker. The SA node generates electrical impulses that travel across the heart muscles, causing them to contract. This process is known as cardiac conduction. The atrioventricular (AV) node helps regulate these impulses, ensuring that the atria (upper chambers of the heart) contract before the ventricles, allowing for proper blood flow.
This electrical conduction system can be compared to the wiring in a house, where electricity flows through circuits, causing lights to turn on and off. If there is a problem in the electrical pathway, such as in the case of arrhythmias (irregular heartbeats), the heart’s rhythm can become erratic, leading to inefficient blood pumping.
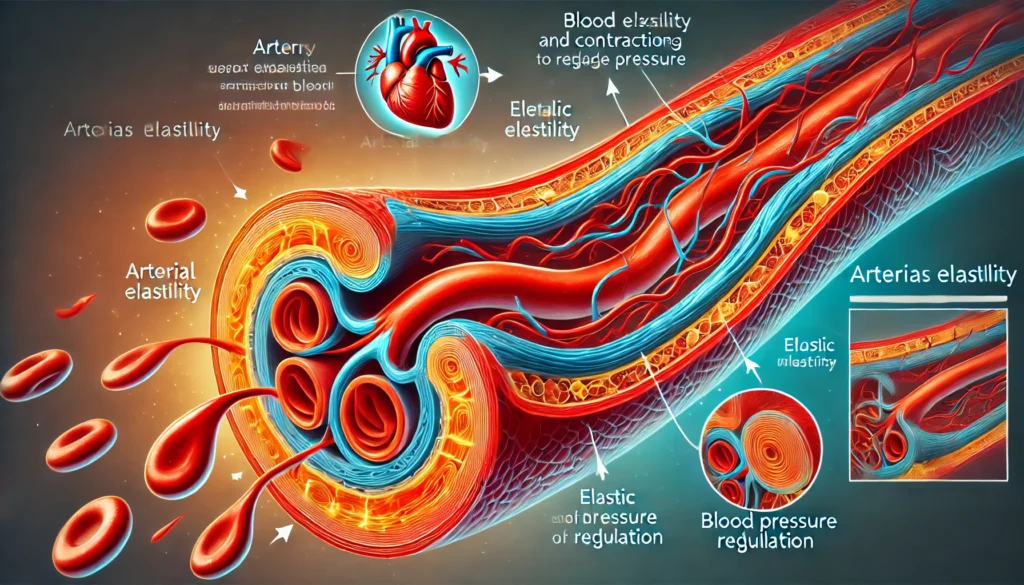
The Role of Elasticity in Arteries
The elasticity of arteries plays a vital role in maintaining proper blood pressure and flow. When the heart pumps blood, the arteries expand to accommodate the surge of blood. Once the heart relaxes, these arteries contract, pushing blood forward. This elasticity allows the arteries to buffer the pressure created by the heart and maintain a steady flow of blood throughout the body. As we age and our lifestyle habits change, arterial flexibility can decrease, leading to stiffened arteries and a higher risk of heart diseases like arteriosclerosis.
Heart Valves: Controlling the Flow of Blood
The heart is equipped with four valves—tricuspid, mitral, aortic, and pulmonary—which regulate blood flow through its chambers. These valves act like doors, ensuring that blood flows in one direction and preventing backflow. The physics of these valves can be compared to a one-way street: they open to allow blood through when the pressure is right and close to prevent any backward movement. When these valves become incompetent or stenotic (narrowed or stiff), the heart must work harder to compensate, which can lead to heart failure or other conditions.
The Concept of Work and Energy in Heart Function
Your heart performs work every time it beats. According to the principles of work and energy in physics, the heart uses energy (primarily in the form of ATP—adenosine triphosphate, a molecule that stores and transfers energy in cells) to pump blood against the resistance in the blood vessels. The harder the heart has to work, the more energy it consumes. This explains why people with conditions like high blood pressure or heart valve disease often feel fatigued; their heart is using up more energy just to keep up with basic functions.
Maintaining Cardiac Health: A Physics-Based Approach
Understanding the physics of heart function opens the door to better managing cardiac health. Below are some key ways to keep your heart functioning efficiently:
Regular Physical Activity
Exercise increases the heart’s efficiency by improving its ability to pump blood. It also strengthens the heart muscle, making it more resilient against stress. Physical activities such as walking, running, swimming, and cycling enhance cardiac output (the volume of blood pumped by the heart per minute) and improve circulation. Think of it as “conditioning” the heart to operate smoothly, just like maintaining a machine so it doesn’t wear out quickly.
A Balanced Diet
Consuming a balanced diet that includes fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats can help prevent plaque formation in arteries, maintain flexibility, and reduce the likelihood of high blood pressure. Omega-3 fatty acids, commonly found in fish, are known to support heart health by decreasing bad cholesterol (LDL) and increasing good cholesterol (HDL).
Stress Management
Prolonged stress can elevate both blood pressure and heart rate, placing additional strain on the heart. Techniques like meditation, deep breathing, and mindfulness can help lower the risk of stress-induced heart problems. It’s essential to remember that stress not only affects the mind but also the physical systems of the body, especially the heart.
Regular Health Check-Ups
Regular blood pressure and cholesterol monitoring can help detect early signs of heart disease. Early intervention can prevent complications and promote long-term cardiac health. Much like how we service our cars to prevent breakdowns, regular check-ups help ensure that the heart is functioning optimally.
Conclusion
The physics of heart function is a marvel of nature. Through a combination of pressure regulation and electrical signalling, the heart operates in sync with physical laws to keep us alive. By understanding these processes and how they affect cardiac health, we can take proactive steps to maintain a healthy heart. Whether it’s through exercise, a balanced diet, or managing stress, our actions can help ensure our hearts keep ticking smoothly for years to come.
Author’s Note
The heart is an incredible organ that we often take for granted. As someone fascinated by the way science influences health, I hope this blog has given you a new appreciation for the physics behind your heart. Take care of your heart, and it will take care of you.
G.C., Ecosociosphere contributor.
References and Further Reading
- Harvard Medical School: Heart Disease
- Premature ventricular contractions (PVCs) – Symptoms & causes – Mayo Clinic. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/premature-ventricular-contractions/symptoms-causes/syc-20376757?mc_id=us&utm_source=newsnetwork&utm_medium=l&utm_content=content&utm_campaign=mayoclinic&geo=national&placementsite=enterprise&invsrc=other&cauid=100721&p=1
- The Fascinating World of Cardiac Anatomy and Physiology | Mantei Ship. https://manteiship.com/25731-the-fascinating-world-of-cardiac-anatomy-and-physiology-19/
- The Cardiovascular System – Ofanziva. https://ofanziva.info/the-cardiovascular-system/


Comments
I抳e learn a few good stuff here. Definitely worth bookmarking for revisiting. I surprise how a lot attempt you place to make this sort of fantastic informative website.