Have you ever wondered if time could slow down or speed up depending on where you are or how fast you’re moving? While it might seem like a concept from science fiction, this is an actual phenomenon explained by Einstein’s theory of relativity. This concept is called “time dilation,” and it challenges our everyday understanding of time. In this blog, we’ll dive into the science behind time dilation in relativity, exploring how it works and what it means for our understanding of the universe.
What is Time Dilation?
Time dilation is a concept that arises from Albert Einstein’s theory of relativity. Simply put, time dilation refers to the idea that time can flow at varying speeds for different observers, influenced by their relative speed or the intensity of the gravitational field they are experiencing. This phenomenon is a cornerstone of both special relativity and general relativity.
Special Relativity:
When objects move at speeds close to the speed of light, time slows down for them relative to an observer at rest. This is known as “relativistic time dilation.” For example, if you were traveling in a spaceship at 90% of the speed of light, you would experience time more slowly than someone on Earth. A journey that seems to last a year for you might appear to take much longer for those left behind.
General Relativity:
Time dilation also occurs due to gravity, known as “gravitational time dilation.” Based on general relativity, the more intense the gravitational field (like near a massive object such as a black hole), the slower time moves relative to an observer far away from the gravitational source.

Real-World Examples of Time Dilation
Time dilation isn’t just a theoretical concept; it has been observed and measured in real-world scenarios.
GPS Satellites:
One of the most practical examples of time dilation comes from the Global Positioning System (GPS). GPS satellites move around the Earth at high velocities and are positioned farther from the Earth’s gravitational field compared to people on the surface. Because of this, their clocks run faster than clocks on the ground. Engineers must account for both the relativistic time dilation due to their speed and the gravitational time dilation to ensure that GPS signals remain accurate.
Muon Decay:
Muons are subatomic particles created when cosmic rays collide with the Earth’s atmosphere. These particles decay very quickly, typically within microseconds. However, muons produced in the upper atmosphere move toward Earth at almost the speed of light. Due to time dilation, these muons experience time much slower, allowing many more of them to reach the Earth’s surface than would be expected if time were passing at the same rate as it does on Earth.
Anecdotal Thought Experiment – The Twin Paradox:
Imagine two identical twins. One embarks on a space journey at near-light speeds, while the other stays on Earth. Upon the traveling twin’s return, they would find their Earth-bound sibling has aged significantly more than they have. This is the essence of the twin paradox, a thought experiment that vividly illustrates time dilation.
The Mathematics Behind Time Dilation
While the concept of time dilation can be explained qualitatively, the mathematics behind it provides a more precise understanding. Let’s take a brief look at the equations that govern time dilation in special relativity.
For special relativity, the time dilation formula is:
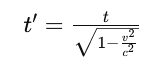
Where:
- t′ is the time observed in the moving frame (e.g., the spaceship).
- t is the time observed in the stationary frame (e.g., on Earth).
- v represents the speed of the object in motion.
- c stands for the speed of light.
As the velocity vvv approaches the speed of light ccc, the denominator approaches zero, which means t′t’t′ becomes much larger than ttt, indicating significant time dilation.
Time Dilation and Its Implications on Our Understanding of Time
Time dilation challenges the notion of absolute time, which is the idea that time passes at the same rate for everyone, everywhere. Instead, time is relative—depending on your speed and gravitational environment. This relativity of time has profound implications for our understanding of the universe.
Time Travel: While time dilation doesn’t imply time travel in the science fiction sense, it does mean that traveling at high speeds could effectively allow someone to “travel to the future” as they would age slower compared to those left behind.
Black Holes and Event Horizons: Near a black hole, time dilation becomes extreme. For an observer far away, time for an object approaching a black hole’s event horizon would appear to slow down infinitely, effectively freezing the object in time at the horizon.
Universe’s Structure: Time dilation also helps explain the large-scale structure of the universe, particularly in understanding how galaxies and other cosmic phenomena evolve over billions of years.
Conclusion
Time dilation is one of the most mind-bending concepts to come out of Einstein’s theory of relativity, fundamentally altering our understanding of time and space. Whether it’s the slowing of clocks on speeding satellites or the strange time effects near a black hole, time dilation shows us that time is not a rigid, uniform flow but something that can stretch, compress, and even stand still under the right conditions.
As we continue to explore the universe and push the boundaries of physics, understanding time dilation will play a key role in managing the challenges of space exploration and uncovering the mysteries of the cosmos. So next time you glance at a clock, remember—it’s not just ticking away seconds, but revealing the deep, intricate dance of space, time, and gravity.
Author’s Note
Exploring the concept of time dilation has always fascinated me, and writing this blog has allowed me to share that passion with you. I hope this piece helps demystify this complex topic and sparks your curiosity to learn more about the universe’s hidden wonders.
G.C., Ecosociosphere contributor.




