Have you ever had a “gut feeling” about something? It turns out, there’s more to that saying than we might think. Welcome to the world of the gut-brain axis, a fascinating conversation between your gut and your brain that impacts your mood, stress levels, and overall health. Imagine your gut and brain chatting over a cup of coffee, exchanging messages that affect how you feel and think. This connection is not just about digestion or hunger; it’s about how the trillions of tiny organisms living in your gut, collectively known as the microbiome, influence your mental well-being.
Think of your gut microbiome as a bustling city, home to diverse microbial inhabitants that help you digest food, fight off diseases, and even manage your emotions. These tiny residents communicate with your brain through various channels, like nerves and hormones, playing a crucial role in your feelings and moods. It’s like they’re sending text messages to your brain, telling it how to feel and react to different situations.
In this post, we’re going to explore this intriguing gut-brain conversation. We’ll look at how these microscopic gut inhabitants can affect our mental health, shed light on the science behind this relationship, and discuss what it means for our daily lives. So, let’s dive into the amazing world of the gut-brain axis, where we’ll unravel how our gut health can mirror our mental state and discover the potential of this link in shaping our mental health. Get ready for a journey into the depths of our bodies, where we’ll find out how taking care of our gut can be a pathway to nurturing our minds.
Scientific Foundations
Let’s get into the science behind this gut-brain chatter. It might sound like science fiction, but it’s all real! Researchers have been piecing together this puzzle, finding out how the tiny organisms in our gut can have a big impact on our mental health. It’s a bit like discovering that the characters in your favorite background music influence the way you feel and think.
- The Gut-Microbiome Link to Mental Health
Researchers have been unraveling the fascinating link between our gut microbiome and mental health. They’ve found that the diversity and balance of bacteria in our gut can significantly affect our mood and mental state. For instance, studies reveal that people with conditions like depression often have a different bacterial makeup in their gut compared to those without these conditions. This discovery suggests a direct correlation between the composition of our gut microbiome and our mental well-being.

- Communication via Chemicals
Our gut bacteria communicate with the brain using some of the body’s chemical messengers. Remarkably, these tiny microbes can produce neurotransmitters, such as serotonin and dopamine, which play key roles in regulating our moods and emotions. This means that the state of our gut can directly influence the production of chemicals that make us feel good or stressed.
- Inflammation and Mental Health
Another critical piece of the puzzle is inflammation. The microbiome has a role in regulating the body’s immune response, which includes controlling inflammation levels. Excessive inflammation has been linked to mental health challenges, including anxiety and depression. By managing inflammation, our gut bacteria can help maintain not only our physical health but also our mental equilibrium.
Understanding these scientific foundations helps us appreciate the complex and intimate relationship between our gut microbiome and mental health. It’s a clear indication that to nurture our minds, we might also need to take care of our gut.
Mechanisms of Influence
- Biochemical Messaging
The gut-brain axis operates like a two-way communication system, where the gut microbes send and receive signals to and from the brain. This communication happens through biochemical messengers, including neurotransmitters like serotonin, which influence mood, appetite, and sleep. Surprisingly, a large portion of the body’s serotonin is produced in the gut, not the brain. This production is influenced by the gut’s microbial inhabitants, which means they have a direct role in regulating our emotions and feelings.
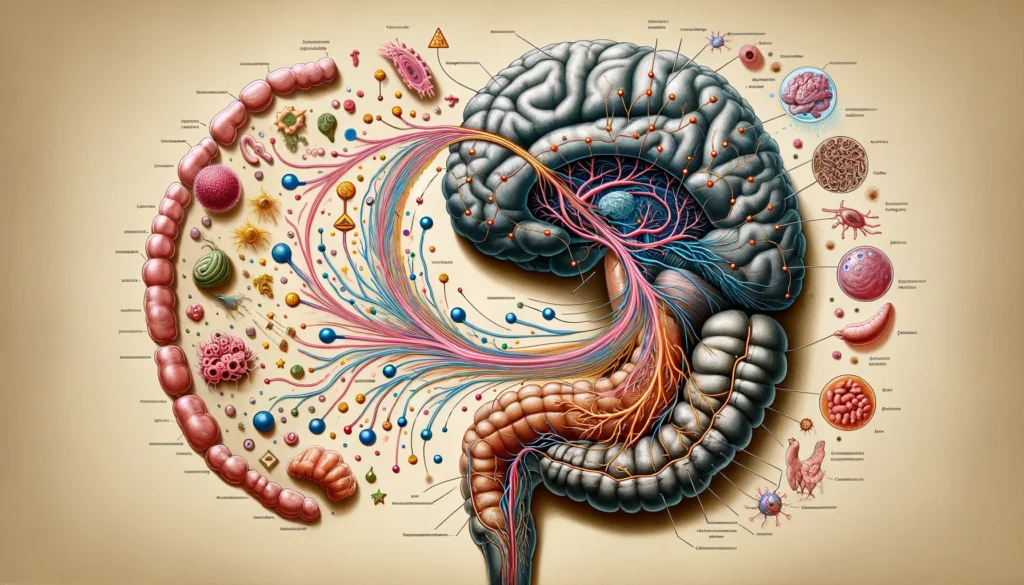
- Nervous System Pathways
The gut microbes also interact with the brain through the nervous system. The vagus nerve, one of the largest nerves connecting the gut and the brain, acts as a major highway for this two-way traffic. Changes in gut microbiota can send signals along the vagus nerve, affecting brain function and emotional state. This pathway helps explain why our gut health can have such a rapid and profound impact on our mental state.
- Immune System Interplay
The relationship between the gut microbiome and the immune system is another key factor in this complex communication network. The gut microbiota helps to regulate the immune system by controlling inflammation, a common underlying factor in many mental health disorders. By influencing the immune response, the gut microbiota can affect brain health and mood, underscoring the deep connection between our immune health and mental well-being.
Through these mechanisms, the microscopic life in our gut exerts a significant influence on our mental health. This intricate dialogue between our gut and brain highlights the importance of microbial health in maintaining mental balance and well-being.
Microbiome and Mental Health Disorders
- Impact on Depression and Anxiety
The connection between gut health and mental health extends to specific disorders, such as depression and anxiety. Research indicates that people suffering from these conditions often have an altered gut microbiome. For instance, certain beneficial bacteria that are less abundant or missing in individuals with depression could be crucial for producing mood-regulating neurotransmitters. This imbalance in the gut microbiota can contribute to the biochemical dysfunction seen in depression and anxiety disorders.

- Gut Microbes and Autism Spectrum Disorders
Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is another area where gut microbiome research has shown promising insights. Individuals with ASD frequently experience gastrointestinal issues, suggesting a strong gut-brain link. Studies have found distinct differences in the microbiome compositions of individuals with ASD, leading to investigations on how modifying the gut bacteria could alleviate some symptoms of autism.
- Potential Pathways for Therapeutic Intervention
Understanding the specific ways in which the microbiome affects mental health disorders opens up new possibilities for treatment. For example, if certain microbes are found to play a role in mitigating anxiety, probiotics containing these microbes could be developed as part of a treatment plan. This approach represents a significant shift towards more personalized and holistic treatments for mental health conditions, emphasizing the role of gut health in mental wellness.
The exploration of how the microbiome influences mental health disorders not only broadens our understanding of these conditions but also offers hope for innovative and effective treatment options. By unraveling the complex interactions between gut microbes and the brain, researchers pave the way for groundbreaking interventions that target the microbiome to improve mental health.
Therapeutic Implications and Future Directions
- Probiotics and Prebiotics: Allies in Mental Wellness
The exploration of probiotics and prebiotics marks a promising frontier in harnessing the gut-brain axis for mental health therapy. Probiotics, the beneficial bacteria, and prebiotics, the fibers that feed them, are being studied for their potential to improve mental health. By altering the composition of the gut microbiome, these supplements can enhance the production of mood-regulating chemicals and reduce inflammation, thereby offering a natural approach to mitigating symptoms of mental disorders.

- Dietary Influence: The Power of Food
Diet plays a crucial role in shaping our gut microbiome and, consequently, our mental health. Foods rich in fiber, antioxidants, and healthy fats can promote a diverse and balanced microbiome, which supports brain health. Future dietary guidelines may increasingly focus on mental wellness, emphasizing foods that foster a healthy gut-brain relationship.
- Personalized Medicine: Tailoring Treatments
The field of personalized medicine is gaining momentum, with the gut microbiome being a key factor in customizing treatment plans. As researchers learn more about the individual variability in microbiome composition, treatments for mental health conditions could become more personalized. This approach might involve specific dietary recommendations, targeted probiotics, or other interventions based on an individual’s unique microbiome profile.
- Future Research and Potential
Ongoing research aims to deepen our understanding of the gut-brain axis and unlock new therapeutic strategies. Future studies will likely explore the efficacy of microbiome-targeted treatments in larger populations and diverse conditions. As the scientific community delves further into the microbiome’s role in mental health, we can expect to see innovative treatments that complement traditional therapies, offering hope for more effective and holistic approaches to mental wellness.
The evolving landscape of gut-brain axis research holds the promise of revolutionizing our approach to mental health, with the potential to develop novel therapies that offer relief and improved quality of life for those affected by mental health disorders.

Conclusion
The exploration of the gut-brain axis reveals a fascinating intersection between microbiology and mental health, showing how the tiny organisms in our gut can have a profound impact on our mental state. This research not only expands our understanding of mental health disorders but also opens new pathways for innovative treatments. By taking care of our gut microbiome, we might find powerful allies in our quest for mental well-being. As we continue to unravel the mysteries of the gut-brain connection, we move closer to a holistic approach to health that integrates body, mind, and microbiome.
Author’s Note
Thank you for joining me on this journey through the gut-brain axis. As we delve into the complexities of our bodies, we uncover the profound impact of our gut microbiome on mental health. I hope that this blog enlightens and inspires you to consider the holistic nature of well-being, where mental health is intertwined with the physical, and every microbe plays a part.
G.C., Ecosociosphere contributor.
References and Further Reading
- “The Psychobiotic Revolution” by Scott C. Anderson, John F. Cryan, and Ted Dinan – A book exploring the connection between gut bacteria and the brain, offering insights into how the microbiome influences mental health.
- “Gut Feelings: The Microbiome and Our Health” by Alessio Fasano and Susie Flaherty – This book discusses the complex relationship between the gut microbiome and overall health, including mental well-being.
- “Brain Maker: The Power of Gut Microbes to Heal and Protect Your Brain–for Life” by David Perlmutter – A book that delves into how gut health can affect the brain, with a focus on preventing neurological disorders.




Comments
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article.
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.